- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
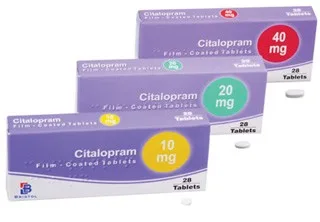
Product
- Canadian Pharmacy Online Pharmacy | Online Canadian Pharmacy
- Need More Information Call Us 1-833-356-6337
Product description
INDICATIONS
Citalopram is used for treating depression. Citalopram is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). It works by restoring the balance of serotonin, a natural substance in the brain, which helps to improve certain mood problems.
INSTRUCTIONS
Use Citalopram as directed by your doctor.
- Take Citalopram by mouth with or without food.
- Taking Citalopram at the same time each day will help you remember to take it.
- Continue to take Citalopram even if you feel well. Do not miss any doses.
- Do not suddenly stop taking Citalopram without checking with your doctor. Side effects may occur. They may include mental or mood changes, numbness or tingling of the skin, dizziness, confusion, headache, trouble sleeping, or unusual tiredness.
- If you miss a dose of Citalopram, take it as soon as possible. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular dosing schedule. Do not take 2 doses at once.
Ask your health care provider any questions you may have about how to use Citalopram.
STORAGE
Store Citalopram at 77 degrees F (25 degrees C). Brief storage at temperatures between 59 and 86 degrees F (15 and 30 degrees C) is permitted. Store away from heat, moisture, and light. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep Citalopram out of the reach of children and away from pets.
Safety information
Do NOT use Citalopram if:
- you are allergic to any ingredient in Citalopram
- you are taking escitalopram
- you are taking or have taken a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) (eg, phenelzine), selegiline, or St. John’s wort within the last 14 days
- you are taking a fenfluramine derivative (eg, dexfenfluramine), an H1 antagonist (eg, astemizole, terfenadine), nefazodone, pimozide, or sibutramine.
Contact your doctor or health care provider right away if any of these apply to you.
Some medical conditions may interact with Citalopram. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you have any medical conditions, especially if any of the following apply to you:
- if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding
- if you are taking any prescription or nonprescription medicine, herbal preparation, or dietary supplement
- if you have allergies to medicines, foods, or other substances
- if you or a family member has a history of bipolar disorder (manic-depression), other mental or mood problems, suicidal thoughts or attempts, or alcohol or substance abuse
- if you have a history of seizures, liver problems, severe kidney problems, stomach or bowel bleeding, or metabolism problems
- if you are dehydrated, have low blood sodium levels, or drink alcohol
- if you will be having electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).
Some medicines may interact with Citalopram. Tell your health care provider if you are taking any other medicines, especially any of the following:
- Fenfluramine derivatives (eg, dexfenfluramine), linezolid, lithium, MAOIs (eg, phenelzine), metoclopramide, nefazodone, selegiline, serotonin 5-HT1 receptor agonists (eg, sumatriptan), sibutramine, St. John’s wort, or trazodone because severe side effects, such as a reaction that may include fever, rigid muscles, blood pressure changes, mental changes, confusion, irritability, agitation, delirium, and coma, may occur
- Anticoagulants (eg, warfarin), aspirin, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (eg, ibuprofen) because the risk of bleeding, including stomach bleeding, may be increased
- Diuretics (eg, furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide) because the risk of low blood sodium levels may be increased
- Tramadol because the risk of seizures may be increased
- H1 antagonists (eg, astemizole, terfenadine) or phenothiazines (eg, chlorpromazine, thioridazine) because severe heart problems, including irregular heartbeat, may occur
- Carbamazepine or cyproheptadine because they may decrease Citalopram’s effectiveness
- Clozapine, pimozide, risperidone, or tricyclic antidepressants (eg, amitriptyline) because the risk of their side effects may be increased by Citalopram.
This may not be a complete list of all interactions that may occur. Ask your health care provider if Citalopram may interact with other medicines that you take. Check with your health care provider before you start, stop, or change the dose of any medicine.
Important safety information:
- Citalopram may cause drowsiness or dizziness. These effects may be worse if you take it with alcohol or certain medicines. Use Citalopram with caution. Do not drive or perform other possible unsafe tasks until you know how you react to it.
- Do not drink alcohol while you are using Citalopram.
- Check with your doctor before you use medicines that may cause drowsiness (eg, sleep aids, muscle relaxers) while you are using Citalopram; it may add to their effects. Ask your pharmacist if you have questions about which medicines may cause drowsiness.
- One to 4 weeks may pass before your symptoms improve. Do NOT take more than the recommended dose, change your dose, or use Citalopram for longer than prescribed without checking with your doctor.
- Children, teenagers, and young adults who take Citalopram may be at increased risk for suicidal thoughts or actions. Watch all patients who take Citalopram closely. Contact the doctor at once if new, worsened, or sudden symptoms such as depressed mood; anxious, restless, or irritable behavior; panic attacks; or any unusual change in mood or behavior occur. Contact the doctor right away if any signs of suicidal thoughts or actions occur.
- Citalopram and a medicine called escitalopram have the same active ingredient. Do not take Citalopram if you are also taking escitalopram.
- If your doctor tells you to stop taking Citalopram, you will need to wait for several weeks before beginning to take certain other medicines (eg, MAOIs, nefazodone). Ask your doctor when you should start to take your new medicines after you have stopped taking Citalopram.
- Citalopram may rarely cause a prolonged, painful erection. This could happen even when you are not having sex. If this is not treated right away, it could lead to permanent sexual problems such as impotence. Contact your doctor right away if this happens.
- Serotonin syndrome is a possibly fatal syndrome that can be caused by Citalopram. Your risk may be greater if you take Citalopram with certain other medicines (eg, “triptans,” MAOIs). Symptoms may include agitation; confusion; hallucinations; coma; fever; fast or irregular heartbeat; tremor; excessive sweating; and nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. Contact your doctor at once if you have any of these symptoms.
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) is a possibly fatal syndrome that can be caused by Citalopram. Symptoms may include fever; stiff muscles; confusion; abnormal thinking; fast or irregular heartbeat; and sweating. Contact your doctor at once if you have any of these symptoms.
- Use Citalopram with caution in the elderly; they may be more sensitive to its effects, especially low blood sodium levels.
- Caution is advised when using Citalopram in children; they may be more sensitive to its effects, especially increased risk of suicidal thoughts or actions.
- Citalopram should be used with extreme caution in children; safety and effectiveness in children have not been confirmed.
- Citalopram may cause weight changes. Children and teenagers may need regular weight and growth checks while they take Citalopram.
- Pregnancy and breast-feeding: Citalopram may cause harm to the fetus if it is used during the last 3 months of pregnancy. If you become pregnant, contact your doctor. You will need to discuss the benefits and risks of using Citalopram while you are pregnant. Citalopram is found in breast milk. Do not breastfeed while taking Citalopram.
Side effects
All medicines may cause side effects, but many people have no, or minor, side effects.
Check with your doctor if any of these most common side effects persist or become bothersome:
Decreased sexual desire or ability; diarrhea; dizziness; drowsiness; dry mouth; increased sweating; lightheadedness when you stand or sit up; loss of appetite; nausea; stuffy nose; tiredness.
Seek medical attention right away if any of these severe side effects occur:
Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue); absent menstrual period; bizarre behavior; black or bloody stools; chest pain; confusion; decreased concentration; decreased coordination; fainting; fast or irregular heartbeat; hallucinations; memory loss; new or worsening agitation, panic attacks, aggressiveness, impulsiveness, irritability, hostility, exaggerated feeling of well-being, restlessness, or inability to sit still; persistent, painful erection; red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin; seizures; severe or persistent anxiety or trouble sleeping; severe or persistent headache; stomach pain; suicidal thoughts or attempts; tremor; unusual bruising or bleeding; unusual or severe mental or mood changes; unusual weakness; vision changes; worsening of depression.
This is not a complete list of all side effects that may occur. If you have questions about side effects, contact your health care provider.